R-Value vs U-Value in Windows Explained
Shopping for new windows or trying to lower your energy bills? You’ve likely seen terms like R-value and U-value pop up — and you likely have no idea what they mean. They are both ratings that deal with how windows manage heat flow, but they work in opposite ways. Having a handle on these ratings can help you pick energy-efficient windows that keep your home cozy year-round. Below, we’ll explain each measurement, why they matter, and how they can guide you toward a smarter window investment.
What Are R-Value and U-Value?
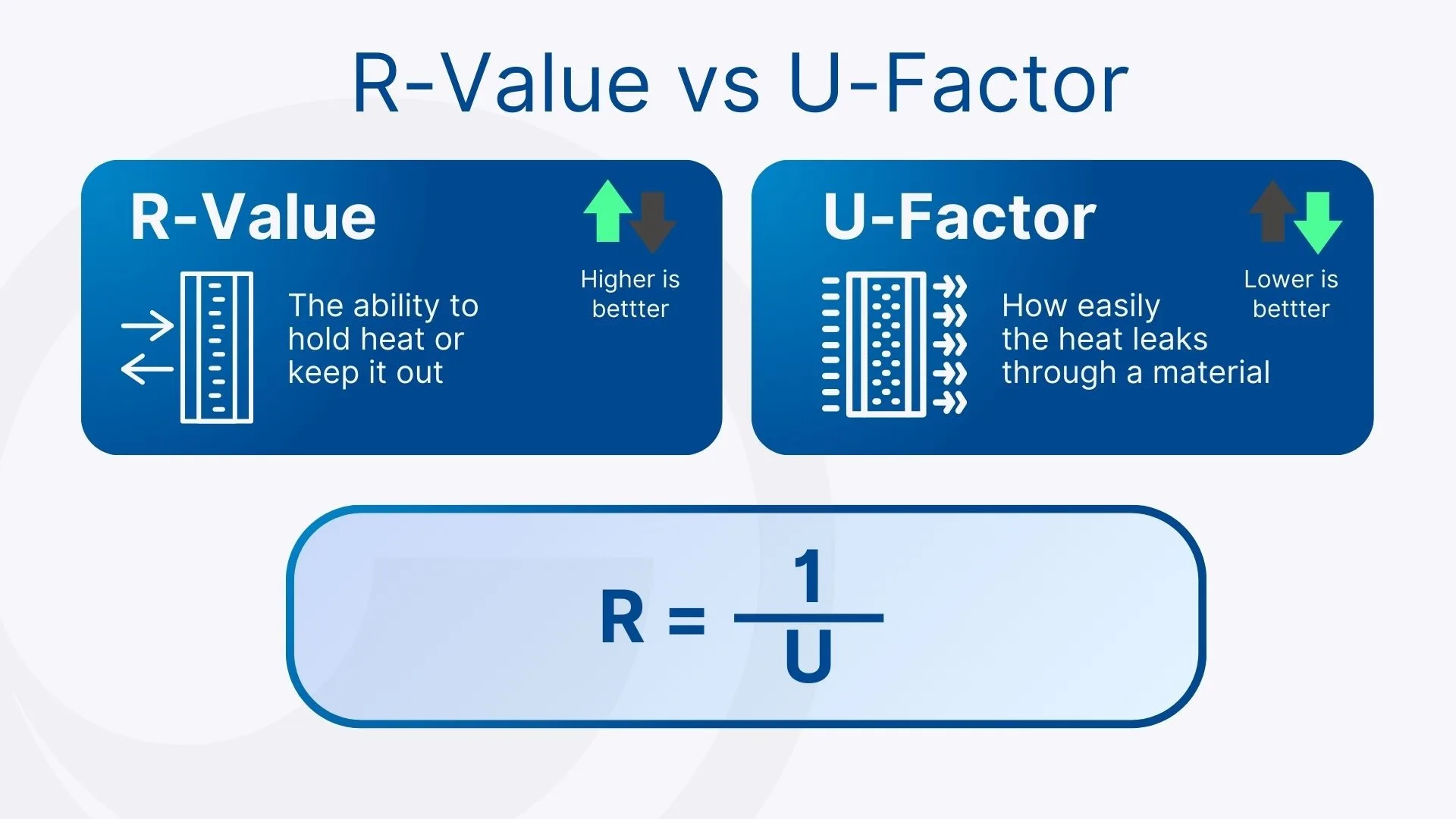
Both R-value and U-factor are measurements of a material’s ability to resist or transfer heat:
- R-value measures a material’s ability to hold onto heat (or keep it out). A higher R-value means stronger insulation.
- U-factor (also called U-value), sometimes called thermal transmittance, measures how easily heat flows through a material. A lower U-factor means the window does a better job of holding in warmth.
When taken together, these two metrics give you a fuller picture of a window’s overall energy performance.
Together, they paint a complete picture of a window’s insulating ability. However, you won’t see R-value on the NFRC label. To convert from U-value, simply divide 1 by the U-value. For example: U-factor 0.26 BTU/(h·ft²·°F) = R-value ≈ 3.85.
R-Value: The Insulation Factor

The R-value measures how well something resists heat flow. Imagine adding layers to a winter coat: every extra layer traps more heat, which increases the R-value.
Factors Affecting R-Value
- Material: Certain materials, like fiberglass or foam, have higher R-values than others.
- Thickness: The thicker the insulation, the higher the R-value.
- Climate zone: The required R-value varies depending on your location and climate.
Why R-Value Matters
Although you often hear about R-values when talking about walls or roofing, window glass can also carry an R-value rating. The higher it is, the more likely you’ll enjoy stable indoor temperatures and lower heating and cooling expenses.
U-Factor: What Does It Measure?

While R-value focuses on resistance, U-value measures the rate of heat transfer through a material. It tells you how much heat energy is lost.
Think of the U-value like a leaky faucet — when the U-value is high, it’s as if more heat is dripping away. Lowering the U-value reduces the amount of warmth lost, keeping indoor temperatures more stable and comfortable.
Factors Affecting U-Value
- Glass configuration: Multi-pane windows (double or triple) generally have lower U-values than single-pane designs.
- Insulating gas fills: Layers of argon or krypton between the panes help reduce heat transfer.
- Low-E coatings: Special coatings cut down on heat loss, which also lowers the U-value.
Why U-Value Matters
A window’s U-value reflects how well the entire system — frame, glass, spacer, and gas fill —retains heat. A lower U-value means greater energy efficiency and, often, reduced heating and cooling costs. In the U.S., U-value is typically measured in BTU/(hr·ft²·°F), so it’s easy to compare windows from different manufacturers.
For example, here are some typical U-values for vinyl windows:
- Double‑pane vinyl windows: U ≈ 0.25–0.29 (R ≈ 3.5–4)
- Triple‑pane vinyl windows: U ≈ 0.14–0.18 (R ≈ 5.5–7)
Now the difference between double- and triple-pane windows suddenly becomes clearer.
R-Value vs U-Value: Key Differences

Let’s review the differences between U-factor and R-value first before you start comparing window options.
1. What They Measure
- R-value measures a material’s resistance to heat transfer (higher is better).
- U-value measures how much heat passes through a material (lower is better).
2. Application
- R-value is typically used for walls, roofs, and insulation products.
- U-value is used to assess windows, doors, and other building components where controlling heat loss is crucial.
3. Units of Measurement
- R-value is expressed as a single number, like R-3 or R-5.
- U-value is expressed in BTU/(hr·ft²·°F).
4. Relevance
- R-value indicates how effectively a material insulates.
- U-value shows the broader level of heat loss through a specific part of the building, such as a window.
Why Windows Need Both R-Value and U-Value

Windows aren’t made of a single material — each unit combines glass, gas fills, coatings, and frames. These elements all affect how much heat is kept inside or outside.
- R-value sheds light on how well the glass itself resists heat flow.
- U-value goes deeper by measuring how the entire window system (frame, glass, spacers, and any gas fills) manages heat transfer.
Looking at both numbers ensures you’re getting a clear view of a window’s overall efficiency.
How to Choose Windows Based on R-Value and U-Value
Balancing R-value and U-value helps you pick windows that work best in your climate and meet your comfort goals.
For Colder Climates
- Focus on high R-value windows to retain heat.
- Look for windows with a low U-value to minimize heat loss.
For Warmer Climates
- Prioritize windows with a low U-value to prevent heat gain.
- Coated glass and gas fills can improve performance in sunny environments.
For Noise Reduction
Although R-value and U-value focus on thermal performance, multi-pane windows with gas fills can also dampen noise. If street traffic or neighborhood sounds are a concern, consider windows with more than one pane and a low U-value.
ENERGY STAR® 7.0 Climate Zones & Targets
Thanks to the Inflation Reduction Act, homeowners who install qualifying windows can claim the §25C tax credit:
- 30% of the product cost (materials only, not installation)
- Up to $600 per year
- Valid through 2032
This turns energy upgrades into real-dollar savings. To qualify, your windows have to meet the latest ENERGY STAR® Version 7.0 standards. Here’s what to aim for based on your location:
| Zone | Max U-Factor | Max SHGC |
|---|---|---|
| Northern | ≤ 0.22 | Any |
| North Central | ≤ 0.25 | ≤ 0.40 |
| South Central | ≤ 0.28 | ≤ 0.23 |
| Southern | ≤ 0.30 | ≤ 0.25 |
In cold climates prioritize high R-values (or low U-values like ≤ 0.25). In hot climates, pair a moderate U-factor (≤ 0.30) with a low SHGC (≤ 0.25–0.30) to block unwanted solar heat.
Not only will this give you tax credits, but you will start saving on energy costs as well.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
Opting for windows with well-balanced R-value and U-value can significantly lower heating and cooling expenses over time.
- Reduced bills: A strong thermal barrier curbs the need for constant heating or air conditioning.
- Environmental benefits: Cutting energy use means shrinking your home’s carbon footprint.
- Long-term returns: Even though efficient windows may cost more upfront, lower utility bills can offset that initial investment.
How R-Value and U-Value Are Tested
Both ratings rely on standardized, controlled methods to keep comparisons fair.
- R-Value: Measured by testing the insulation properties of specific materials under uniform conditions.
- U-Value: Accounts for the window assembly as a whole — glass, frame, spacers, and any coatings or gas fills.
Common Misconceptions About R-Value and U-Value
It’s easy to mix these terms up, so here’s some clarity:
- “A single number tells me everything”. Both R-value and U-value matter. One number alone won’t give the full picture of a window’s efficiency.
- “Always go for the highest R-value”. In warmer areas, the U-value may have a bigger impact on comfort and energy savings.
- “All windows have the same performance”. Frame materials, coatings, and multiple panes can greatly change how well a window insulates.
- “A window with a good R-value must also be soundproof”. R-value and U-factor measure thermal performance — not sound. For noise, look for STC (Sound Transmission Class) or OITC (Outdoor-Indoor Transmission Class) ratings. Multi-pane windows help but ask specifically about acoustic ratings if soundproofing is a concern.
Table of Contents
Keep in Mind R-Value and U-Value to Choose the Better Windows

Selecting high-quality windows means weighing their R-value and U-value together. These two numbers work in tandem to show how effectively a window resists and limits heat flow. Striking the right balance helps create a more comfortable home, lowers energy costs, and boosts long-term value.
If you’re ready to upgrade to windows designed for strong thermal performance, consider GEALAN’s German-engineered solutions. Our products deliver durability and impressive insulation, which can translate into lower bills and a more sustainable lifestyle. Connect with us today to find a local supplier who can guide you toward the best choice.
FAQs
What is the main difference between R-value and U-value?
R-value indicates how well a material resists heat flow (higher is better), while U-value measures how much heat travels through the entire window (lower is better).
Why is U-value more important for windows?
U-value captures heat transfer through not only the glass, but also the frame, spacers, and gas fills, painting a more complete picture of how a window handles warmth and drafts.
What is a good U-value for windows?
In most climates, a U-value below 0.30 BTU/(hr·ft²·°F) is often considered energy-efficient.
How can I improve my window’s U-value?
Adding gas fills (like argon), applying Low-E coatings, or choosing double- or triple-pane designs are good ways to lower your window’s U-value.
Are R-value and U-value related?
Yes. A higher R-value typically means a lower U-value, and vice versa, since both deal with heat flow.


